近期在看鸟哥的博客的时候,发现自己对PHP内核方面还真是一窍不通,就以PHP变量来说,一直都知道PHP变量是写时复制,但是真的去分析这个变量的refcount和is_ref的时候,又是一脸懵逼,学习道路漫漫,戒骄戒躁。
PHP7和PHP5的zval结构具有不同,这里分开来理解
PHP5
zval结构
1 | struct _zval_struct { |
一个变量在创建的时候创建了一个结构体,这个结构体里面的
- value 代表的这个变量的值,
- refcount用于标识此zval被多少个变量引用,当值为0的时候会被销毁
- is_ref标识是不是用户使用 & 的强制引用
赋值
我们以下面的代码为例
1 | <?php |
首先 第一行代码创建了一个变量,并申请了8个字节大小的内存,(这里暂不考虑结构体的其他占用)
第二行又创建了一个变量,与第一个变量 $val 相同,则此时是否应该占用16个字节呢
实际情况并不是这样的,这也就是 结构体中的 refcount 和 is_ref 的作用
我们使用 xdebug_debug_zval 调试一下变量
1 | $val = 'tyloafer' |
这里并没有新申请一块内存,复制结构体,而是将原有的refcount 进行了 +1 操作,那如果此时对变量进行unset操作,其实就是对refcount 进行 -1 操作了
引用赋值
在PHP里面,还有一种赋值方式,即引用赋值,我们以下面代码为例
1 | <?php |
调试变量结果
1 | $val = 'tyloafer' |
这里不仅 refcount 进行了 +1 操作, is_ref 也进行了 +1 操作,因为我们这里使用了 & 操作
针对于 赋值 操作,val 和 ref 两个变量均是指向同一个 zval 结构体,当我们对 ref 进行修改的时候,这时候两个变量的值就会不一样
1 | <?php |
从而可以推断,当执行到 $ref = 1 的时候, ref 和 val 两个变量指向的就不是同一个 zval 结构体了,此时 debug 结果如下
1 | $val = 'tyloafer' |
这个过程就被称作 写时复制 (Copy On Write)
写时复制(Copy On Write)
PHP在修改一个变量以前,会首先查看这个变量的refcount,如果refcount大于1,PHP就会执行一个分离的例程。这个机制就是所谓的copy on write(写时复制)。
其中赋值函数如下
1 | static inline zval* zend_assign_to_variable(zval **variable_ptr_ptr, zval *value TSRMLS_DC) |
这里的EXPECTED(var) 就相当于 val == 1
我们根据这个特性,做一下 下面的代码的分析
1 | <?php |
首先代码执行到第一行 $val = 'tyloafer'; , 这时候 PHP会创建一个zval结构体,此时他的值应该是
refcount = 1, is_ref = 0
执行到第二行的时候,根据上面结果可以知道
$val : val: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=’tyloafer’
$ref : ref: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=’tyloafer’
接下来执行第三行,此时val 的 refcount = 2, is_ref = 1, 满足了写时复制的条件, 但是这里是使用val 的变量,赋值给新的变量,是否会 触发 COW 呢,其实是会触发的,我们照此思路处理下去的话
如果这个脚本就 $copy = $val; 一行的话, 这两个变量 val copy 是会共用一个 结构体的,但是此时 val 结构满足了 分离的条件,所以 这两个变量就需要进行分离,也就是 copy 不能共用 val 的结构体 分离出去,但是原先的 val 和 ref 没有修改, 所以不会触发分离的条件,所以 此时的结果就是
$val : val: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=’tyloafer’
$ref : ref: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=’tyloafer’
$copy : copy: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=’tyloafer’
最后一步, $copy = 111; ,此时的copy 已经分离出来了,是个独立的结构体,也不满足分离条件,直接修改 结构体里面的 value即可
$copy : copy: (refcount=1, is_ref=0)=’1111’
$val : val: (refcount=2, is_ref=1)=’tyloafer’
经典性能问题
1 | <?php |
鸟哥的博客里,针对这个写个一个比较简单的例子,但是我感觉用的最多的场景还是 函数套函数 的场景,所以自己修改了一下 案例
输出结果:
1 | 引用传值共消耗: 1.7663018703461 s |
根据 zend_assign_to_variable 的函数逻辑及上面的分析,就可以看出来是因为复发了 分离 的操作,所以会 拷贝 $i 次数组,这个问题在PHP7的时候已经做了修改。
PHP7
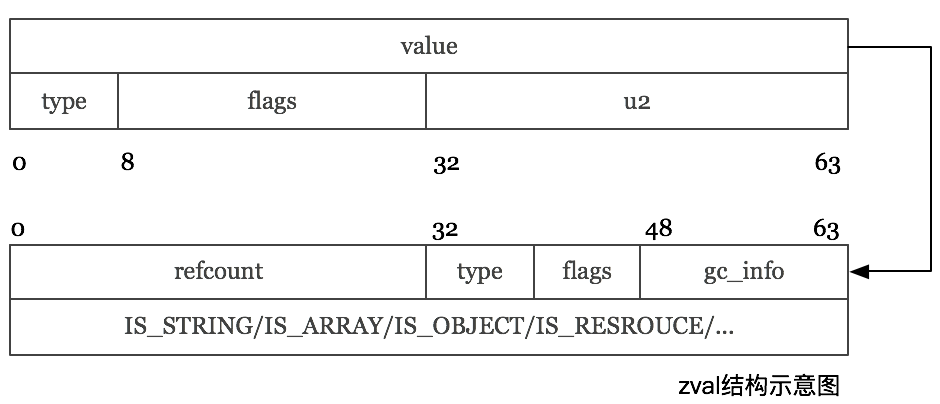
zval结构
1 | struct _zval_struct { |
而引用计数部分保存在 zend_refcounted_h 的结构体中
1 | typedef struct _zend_refcounted_h { |
也即如图所示
写时改变(Change On Write)
1 | <?php |
以上面代码为例
当代码执行到第二行 $ref = &$val; 的时候, 生成一个 IS_REFERNCE 类型,然后因为此时有俩个变量引用它所以zend_reference这个结构的引用计数zval.value.ref->gc.refcount为2.
当代码执行到 $copy = $val; 的时候, 发现 $val 是一个引用, 于是,直接让 $copy 指向的是zval.value.ref->val, 也就是字符串值为laruence的zval, 然后把zval的引用计数+1, 也就是zval.value.ref->val.value.str.gc.refcount为2. 并没有产生复制.
xdebug结果
1 | $val = 'laruence' |